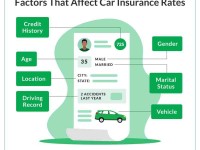
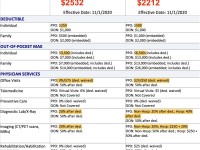
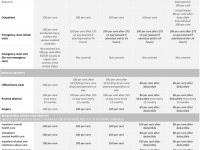
Co Insurance – The collateralization effect is an economic theory that suggests that mergers and acquisitions (M&As) reduce the risk of any combined entity holding debt. According to this theory, one would expect increased diversification due to acquisition activities to reduce borrowing costs for the combined entity.
The coinsurance effect shows that firms involved in mergers and acquisitions benefit from increased diversification. This increase in diversification comes from a broader product portfolio or an expanded customer base.
Contents
- Co Insurance
- Definitions And Meanings Of Health Care And Health Insurance Terms
- Health Insurance Terminology
- What Is Coinsurance
- The 5 Costs That Make Up Your Health Plan
- Commercial Health Plans’ Transition From Copays To Coinsurance And Deductibles Has Increased Patient Out Of Pocket Costs For Brand Medicines
- What Is Coinsurance? 9 Mysteries Of Health Insurance—solved
- What’s The Difference Between Coinsurance And A Copay?
- What Is A Coinsurance? Health Insurance Explained
- Gallery for Co Insurance
- Related posts:
Co Insurance

Even when the acquiring company assumes the debts of another company, the financial strength of the merged entity is theoretically better protected against default than either company. Therefore, the coinsurance effect suggests that the merging firms will experience economic synergy through the combination of operations.
Definitions And Meanings Of Health Care And Health Insurance Terms
A reduction in its debt default risk should reduce investor demand for a company’s bond issues. Bond yields rise and fall depending on the level of repayment risk that bondholders take to finance a business’s debt. Because consolidation should be financially safer, it can lower the cost of issuing new debt, making it cheaper to raise additional capital.
Lower yields may make the issue less attractive to bondholders who will seek higher rates of return to offset the risk.
Suppose a company has commercial real estate concentrated in a certain metropolitan area. Commercial lease income streams will generally be at risk in a regional economic downturn. For example, if a large employer goes out of business or moves to a different area, the reduced economic activity could significantly affect local stores, restaurants and other businesses, reducing overall regional profits. And maybe some businesses may even close.
A less vibrant shopping area will affect the business with lower occupancy rates. This, in turn, will mean less revenue, therefore increasing the likelihood of a commercial real estate company defaulting on its loan.
Health Insurance Terminology
Now suppose that the same company has acquired another commercial real estate unit in a different area. The risk of an unexpected economic downturn in both sectors at the same time is less than the chance that one or the other will experience problems.
There is a greater chance that revenue from one of the two regions would keep the combined company afloat if the other region fell on hard times. Risk reduction implies that the company will be able to issue debt at a lower interest rate after the acquisition because the probability of debt default is reduced by the geographic diversification gained in the merger.
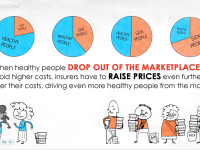
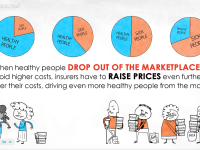
Studies of the coinsurance phenomenon reveal a countervailing force in merger and acquisition (M&A) activity, sometimes called the diversification discount. This effect suggests that investors may adopt a neutral approach to diversification in some cases. These events may include negative public attitudes toward the union, concerns about the different management styles of the larger entity, and a lack of transparency in the mergers and acquisitions process.

In these cases, despite increased post-merger revenue, the resulting share price may be at a discount. Some economists believe that this effect can reduce or even cancel out the coinsurance effect in some cases.
What Is Coinsurance
The offers shown in this table are from partnerships that receive compensation. This compensation may affect how and where listings appear. This does not include all the offers available in the market.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree to the storage of cookies on your device to improve website navigation, analyze website usage and assist in our marketing efforts. The world of insurance can often be confusing. With so many specific terms, it can be easy to get overwhelmed. An important term to be aware of is coinsurance. You’ve probably heard this term before, but what does it mean?
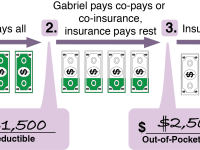
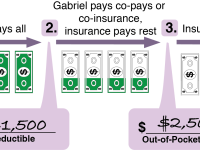
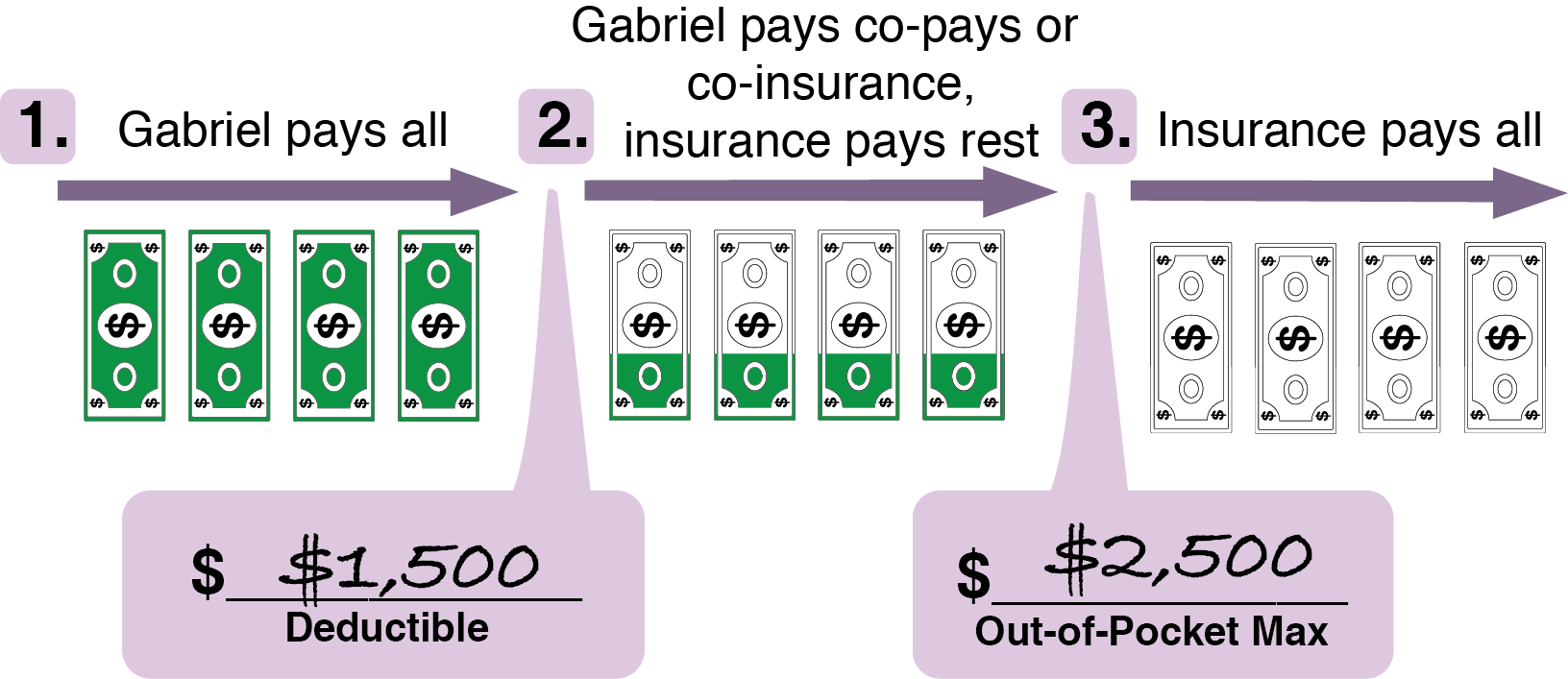
Simply put, this is the cost you share between you and the insurance company after your deductible is met. Your deductible is the amount you pay before your insurance plan begins.
For example, let’s say you’ve paid your deductible. You have a dentist appointment that costs $200. If your coinsurance is 20%, that means you’ll only pay 20%, or $40 in this case.
The 5 Costs That Make Up Your Health Plan
One thing to keep in mind when looking at employee benefits is the relationship between monthly premiums and coinsurance. If your monthly premium is high, your coinsurance will likely be low. If your premium is low, your coinsurance is likely to be high.
Brian led branding and media communications at FBS and leads the marketing department as Director of Marketing. As a top 1% graduate of the UT Arlington Class of 2011, Brian emphasizes excellence and ingenuity, keeping FBS at the forefront of for-profit education and enrollment.
Russ joined FBS in 2019 after serving as a valued partner for 15 years and manages our ISD group health program. Russ holds a Life, Casualty and Health Insurance license and a Risk Management license through the Texas Department of Insurance and brings over thirty years of risk management and pool management experience to FBS. Russ continues to support districts across the state with their risk management programs.
Stacia has been with Financial Benefit Services since 2014 and has 5 years in Insurance Billing and Accounting and a Bachelor of Science in Business Administration from UT Dallas. He and his team will provide monthly billing services to the district. As Billing Manager, she assists with the day-to-day accounting processing of her team and is available to handle any escalating billing issues. Stacia will appoint and work with an FBS Billing Coordinator to work with the District on bundled charges, variances and other billing matters.
Commercial Health Plans’ Transition From Copays To Coinsurance And Deductibles Has Increased Patient Out Of Pocket Costs For Brand Medicines
Kathy has been in the insurance industry for 28 years. Her previous insurance experience includes marketing supervisor, account management and account executive roles with one of the largest insurance carriers for some of the largest employers in the state of Texas. As an Account Executive, he was a key member of the TRS-ActiveCare account team from inception through the duration of the contract. As Director of Client Services at FBS, Kathy oversees the billing, client service and account executive teams and is available to assist with escalated cases if necessary.
Coby joined FBS in 2007 as a benefits consultant and then became vice president of sales in 2013. Koby now manages a team of sales, marketing and customer implementation staff as FBS Senior Vice President. He is a graduate of Texas Tech University and holds several different licenses in the insurance industry, including an insurance advisor license through the Texas Department of Insurance. He currently serves as a benefits consultant for several FBS benefit cooperatives and several independent school districts.
Kyle was hired by FBS in 2001 as one of our first benefits consultants and became President of the company in 2005. Mr. James began his insurance career with American Fidelity in Lubbock, Texas in 1993 and remained with them until 2000 .He is a graduate of Texas Tech University with a degree in Education. Mr. James holds several different licenses in the insurance industry, including an Insurance Counselor License through the Texas Department of Insurance. He currently serves as a benefits consultant for 15 of the 20 Educational Service Centers in the state of Texas. Co-reinsurance is a contractual agreement for two or more reinsurers to share the premiums and potential costs of coverage.
Insurers contract with reinsurance companies to accept a portion of the cost of claims in major events such as hurricanes. Because of the extremely high potential costs of some catastrophes, reinsurance companies sometimes choose to reduce their risks by partnering.
What Is Coinsurance? 9 Mysteries Of Health Insurance—solved
Hurricane Katrina is the costliest disaster in American history, causing approximately $172.5 billion in damages in 2005. Hurricane Harvey in 2017 was not far behind with $133.8 billion in damages.
That record could fall due to the COVID-19 pandemic, which is expected to cost health insurers up to $547 billion by the end of 2021.
This makes it less surprising that insurance companies sell some of their larger risks to reinsurance companies, which in turn may choose to pool their resources to provide co-reinsurance. Insurance companies pay a portion of the premium for the contract to the reinsurers, who split the proceeds and risk pro rata.

This also effectively reduces the risk to the insured, as a Katrina-sized event could bankrupt any insurer.
What’s The Difference Between Coinsurance And A Copay?
Co-reinsurers are often relatively small companies that cannot afford the level of risk required by the contract.
Coinsurance agreements are usually negotiated between the original insurance company, called the ceding company, and a large reinsurer. The primary reinsurer makes decisions on behalf of other reinsurers, called follower reinsurers, who are parties to the coinsurance contract.
The amount of loss for which each reinsurer is liable is generally calculated pro rata, with reinsurers with a larger share of the contract liable for a larger proportion of any claim. In addition to a pro rata share of any losses, co-insurers receive a pro rata share of the premiums they receive for assuming the risk.
In some cases, the coinsurance is not proportionate. Under this scenario, reinsurers would only have to pay out if the insurer faced total claims
What Is A Coinsurance? Health Insurance Explained
Pet insurance co, home insurance co, wright and co insurance, home owners insurance co, co op insurance nyc, car insurance quote co, co op insurance quote, whole life insurance co, cheap insurance co, direct general insurance co, best car insurance co, pacific life insurance co